Precise Digital is the nation’s leader for interview recording systems and equipment, but recordings have come a long way since the world’s first recording.
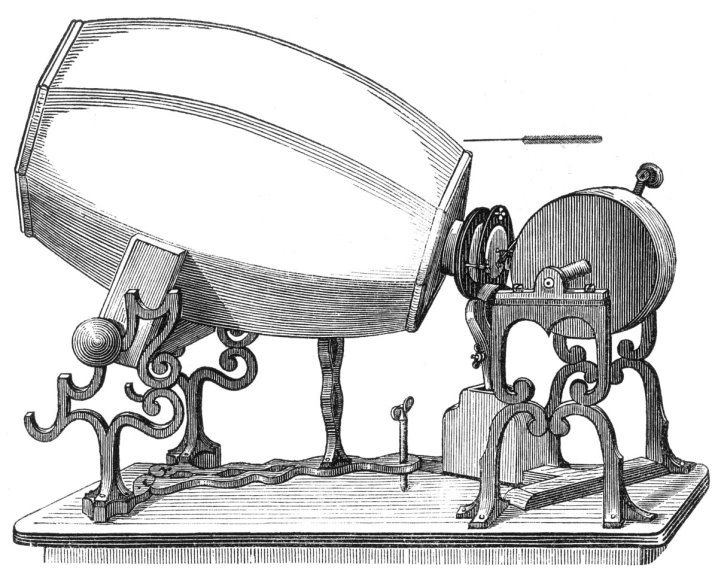
The phonautograph is the earliest known device for recording sound, it was invented by Frenchman Édouard-Léon Scott de Martinville and was patented on March 25, 1857. It transcribed sound waves as undulations or other deviations in a line traced on smoke-blackened paper or glass. Intended solely as a laboratory instrument for the study of acoustics, it could be used to visually study and measure the amplitude envelopes and waveforms of speech and other sounds, or to determine the frequency of a given musical pitch by comparison with a simultaneously recorded reference frequency.
Apparently, it did not occur to anyone before the 1870s that the recordings, called phonautograms, contained enough information about the sound that they could, in theory, be used to recreate it.
Several phonautograms recorded before 1861 were successfully played as sound in 2008 by optically scanning them and using a computer to process the scans into digital audio files.